
Aftercare is the extended care given to a patient after they are released from a hospital, an urgent care clinic, or another type of healthcare facility. It can be viewed as a new phase in the patient journey.
Salesforce Omni-Channel is a workflow function that can be used to streamline patient aftercare and reduce operating costs. Once a patient has left a facility, it’s important to have a system in place that efficiently manages inbound patient requests. Examples of aftercare contact center functions include:
- Referring a patient to a primary care physician
- Referring a patient to a specialist for follow up
- Answering general care questions
- Booking a physical therapy appointment for a patient
- Providing lab results
- Obtaining prescription authorization for a patient
- Relaying X-ray results
Cloud technology can be used to efficiently connect a patient with the right team or right individual at the right point in the continuum of care.
What is Omni-Channel?
Salesforce Service Cloud is software that’s used by contact centers in healthcare, life sciences, and other industries. Omni-Channel is a configurable component of Service Cloud.
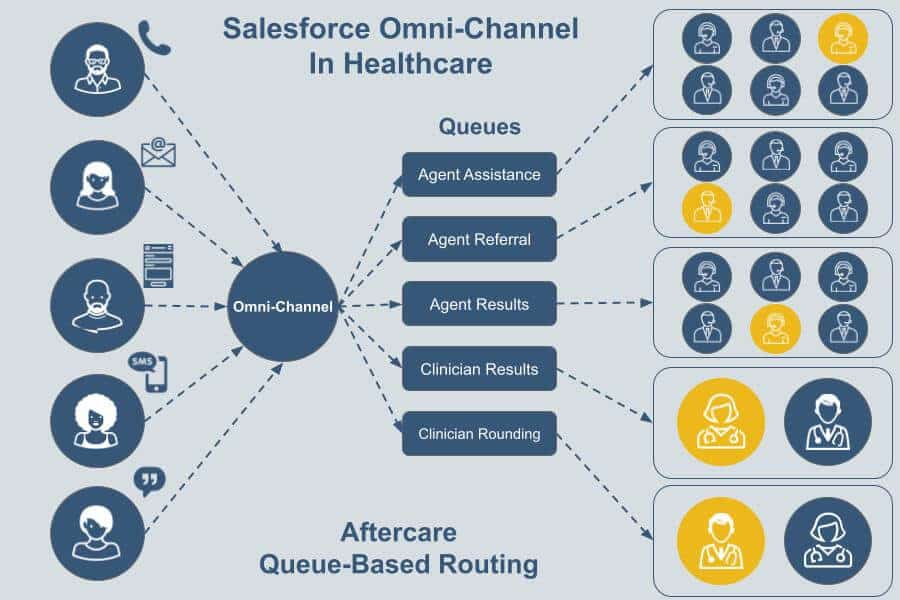
In healthcare, Omni-Channel can be regarded as an inbound routing system that matches a patient’s requests with the right clinical or non-clinical individual. The application is so-named because the service channels that aftercare patients use can include phone, email, web forms, web chat, text messaging, and social media posts. In other words, any and all channels are supported.
These channels all get equal treatment by the system in terms of how a patient request is routed.
Omni-Channel routes patients to the most qualified (and currently available) clinical or non-clinical individuals, using routing criteria defined within a Salesforce customer’s org (database).
There are several ways a patient is routed to the right person. These methods can co-exist.
Queue-Based Routing
Let’s say a healthcare call center has three non-clinical agents who specialize in referring patients to physicians. These specialists are assigned to a queue in Salesforce that’s named “Agent Referrals.” On a given day, two of the agents are on shift.
A recently discharged patient sends an email to the aftercare contact center asking about a referral to a primary care physician. The patient’s email request is considered a work item. The work item is part of a Case (a.k.a. Ticket) in the Salesforce database, which is assigned to the Agent Referral queue.
Rather than a referral specialist having to select a waiting work item from a queue, Omni-Channel can automatically route the Case to an available referral specialist who is a member of the Agent Referral queue.
For each patient, Salesforce Service Cloud determines the best route for the patient’s request. When needed, the routing system can be modified on the fly to adapt to changing patient needs and business requirements.
Skills-Based Routing
Skills-based routing routes a patient to the best individual to handle their request or need. This type of routing applies to both non-clinical and clinical cases.
In the software, each agent or clinician is assigned a set of skills. Inbound requests can then be intelligently routed to the right person. Routing examples are as follows:
Non-Clinical Example of Skills-Based Routing
A Spanish-speaking patient has requested a referral to a specialist because of concerns about ongoing symptoms of a recent ankle injury. The patient’s request can be routed to an agent who has the skills “Spanish speaker” and “referrals to specialists.”
Clinical Example of Skills-Based Routing
A patient’s request is specific to the results of a recent CT scan. The request is routed to an available clinician with the skill “radiologist.”
Custom Routing Rules
Custom routing rules can be created to ensure that time-sensitive requests are handled as quickly as possible. For example, if a patient request is routed to a cardiologist and the request is not picked up within a specified number of minutes, the request can be rerouted to a high-priority clinician queue.
Manual Routing
There are times when a contact center agent needs to reroute a patient work item from themself to a specific doctor, STAT.
If a patient calls in and reports symptoms that may be signs of a complication, the answering agent can immediately route the patient to an available physician’s direct line for triage.
Other Service Cloud Functionality
In addition to managing inbound patient requests with Omni-Channel, Salesforce Service cloud can be used to ensure proactive outbound follow-up with a patient.
For example, a call center agent can be assigned an activity to follow up with a patient two days after they were discharged from the facility.
Service Cloud can also be integrated with EHR systems so that a Service Cloud patient record includes notes from clinical encounters. Lab and radiology results can also be made available in the Service Cloud patient record.
If physician referrals are managed in a separate patient referral management system, that system can also communicate with Service Cloud.
The combination of Omni-Channel, activity management, and systems integration, gives Service Cloud a strong candidate for a patient aftercare system.
J2 Interactive is an award-winning software development and IT consulting firm that specializes in customized solutions for healthcare organizations.
If you would like to learn more about Omni-Channel and Service Cloud for healthcare & life sciences, please get in touch with us.



